The planet is heating up—and so are our bodies. Climate change is no longer a distant concern; it’s a daily reality. From record-breaking heatwaves to unseasonal storms, extreme weather is affecting our health in ways we never imagined. For women over 50, this shift poses unique challenges—especially when combined with menopause, age-related changes, and existing health concerns. Staying healthy today means learning to adapt not just to our changing bodies, but also to a rapidly changing world.
The Science Behind the Heat
Global Warming Is Real—and Rising
According to NASA, the Earth’s average surface temperature has risen by about 1.2°C since the late 19th century, mainly due to increased carbon dioxide and other emissions from human activity.
Source: NASA Climate
This might sound small, but its effects are massive. Higher temperatures lead to more frequent and intense heatwaves, poor air quality, and disruptions to food systems. For older adults, these changes significantly increase the risks of heat-related illnesses and chronic health issues.
How Extreme Weather Affects Our Bodies
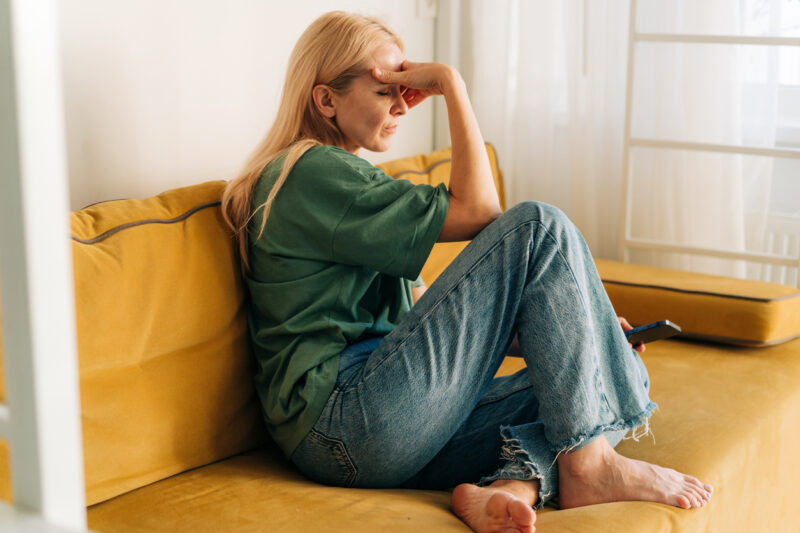
When the temperature rises, your heart works harder to keep your body cool. This can lead to dehydration, dizziness, fatigue, and even heatstroke. For women over 50—especially those managing menopause or other age-related conditions—this stress can be even more dangerous.
Why Women Over 50 Are at Higher Risk
Hormonal Changes and Heat Sensitivity
Menopause comes with natural declines in estrogen, which impacts your body’s ability to regulate temperature. Hot flashes become more intense in summer heat, and night sweats can lead to disrupted sleep and long-term fatigue.
Preexisting Conditions and Aging Organs
As we age, our body becomes less efficient at cooling itself. Add to that common concerns like high blood pressure, reduced bone density, or slower metabolism, and you have a body less able to respond to environmental stressors.
Mental and Emotional Strain
Climate anxiety is real—and it can impact older adults too. Rising temperatures and natural disasters can disrupt routines, limit mobility, and even contribute to depression and anxiety, especially among those living alone or with limited support.
Practical Health Tips for Hotter Days
Stay Hydrated—and Eat Water-Rich Foods
Drinking water is essential, but so is eating foods like cucumber, watermelon, and leafy greens. These not only hydrate but also provide vitamins and minerals that support skin, bones, and cardiovascular function.
Dress for the Climate
Choose light, breathable fabrics like cotton or linen. A wide-brimmed hat and UV-protection sunglasses aren’t just fashion statements—they’re tools for health.
Rethink Exercise
Instead of midday walks or runs, aim for early mornings or after sunset. Indoor yoga, tai chi, or resistance band workouts can keep you moving safely.
Improve Your Indoor Environment
Use fans, air conditioning, or even simple methods like placing a bowl of ice in front of a fan. Keep blinds closed during peak sun hours to reduce indoor temperatures.
Supporting Hormonal Balance Naturally
As the body’s internal balance becomes more vulnerable, supporting hormonal health becomes key. Natural solutions like fermented soy isoflavones can gently ease the effects of menopause while helping regulate temperature sensitivity and fatigue.
One such solution is Juveriente® Effisoy, a supplement based on traditional Japanese dietary wisdom. Its key ingredient—fermented soy isoflavones in aglycone form—supports your body’s ability to produce DHEA, a precursor to estrogen. This helps restore internal balance without synthetic hormones or harsh stimulants.
How Climate Change Affects Your Nutrition
Changes in Crop Quality and Availability
Rising CO₂ levels can reduce the nutrient density of staple crops like rice, wheat, and vegetables. This means even a “healthy” diet may be lacking key minerals like zinc and iron.
Learn more from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Eating Seasonally and Locally
Choosing seasonal, locally grown produce ensures better freshness, nutrition, and lower carbon footprint. Bonus: seasonal foods are often cheaper and richer in flavor.
Building Resilience: Community, Nature, and Mindset
Connect with Others
Whether it’s a walking group, gardening club, or online wellness forum, social connection boosts resilience. Shared knowledge and support can also offer new coping strategies.
Embrace Nature—Safely
Morning walks in shaded parks, gardening at dusk, or even tending to indoor plants can reduce stress and increase your sense of wellbeing.
Stay Informed, Not Overwhelmed
Follow credible sources like the CDC’s Climate and Health Program to stay updated on weather alerts and health precautions. Awareness helps reduce fear and promotes action.
Final Thoughts: It’s Time to Adapt—Gracefully
For women over 50, adapting to climate change isn’t just about surviving the heat. It’s about thriving despite it—by tuning into your body, embracing natural solutions, and nurturing a healthy lifestyle that supports both physical and emotional well-being. Aging and climate change may be inevitable, but with the right knowledge and care, you can face both with resilience and grace.
Take Effisoy®, a natural supplement, to balance your hormone back.
If you are facing an age-related hormonal imbalance, rebalancing it will work with a balanced diet for your beauty, weight management, and daily wellness.
Juveriente®’s Effisoy, launched in 2016, based on fermented soy bean germ extract has been loved as a natural menopause relief since its launching in 2016.
Its primary function is to boost the weakened synthesis of a hormone precursor, DHEA. It helps the precursor, DHEA. Rebalancing the precursor will eventually recover your hormones in line with your natural balance. It will help recover the hormonal imbalance and help you address various issues in postmenopausal period.
Here are some of the real product reviews in our Amazon shop.
“Restful sleep finally!!”, “I Am Now Free of Hot Flashes!!”, “Lifesaver”