Understanding Bone Health: Why Strong Bones Matter
Strong bones are the foundation of a healthy and active life. They provide structure, support movement, and protect vital organs such as the heart and lungs. Maintaining bone strength is essential, especially as we age, to prevent issues like osteoporosis and fractures. When considering which type of exercise contributes most to building strong bones, it’s important to first understand the role bones play in overall health.
The Role of Bones in the Body
Bones are living tissue that constantly renews itself. They store crucial minerals like calcium and phosphorus, which help maintain the strength and function of other systems in the body. Bones also allow us to move by providing a framework for muscles to attach to, enabling everyday activities like walking, lifting, and running. Strong bones ensure that these movements are fluid and safe.
The Impact of Aging on Bone Health
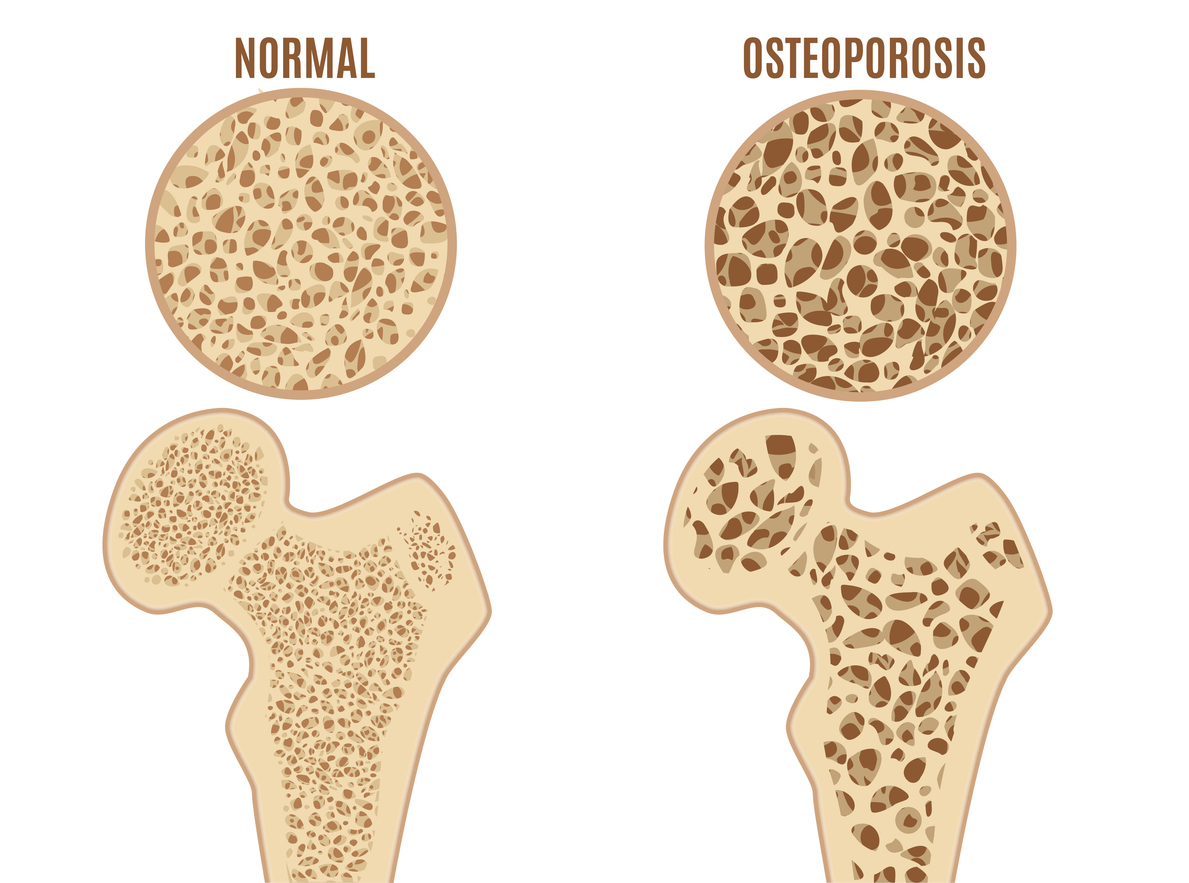
Bone mass peaks in our late 20s, after which it naturally begins to decline. This gradual loss of bone density increases the risk of fractures and conditions such as osteoporosis, especially in older adults. However, bone loss is not inevitable. With the right lifestyle choices—particularly through proper exercise and nutrition—you can maintain and even improve bone density as you age.
Exercise and Bone Strength
Regular physical activity plays a critical role in building and maintaining bone health. Different types of exercise have varying effects on bones, which leads us to the question: which type of exercise contributes most to building strong bones? Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have been proven to be particularly effective at promoting bone density and strength. Understanding these exercises can help you take proactive steps to support long-term bone health.
By prioritizing bone health early in life, you can ensure mobility and strength as you age. Next, we’ll explore the best exercises to incorporate into your routine for building strong bones.
Which Type of Exercise Contributes Most to Building Strong Bones?
When it comes to strengthening bones, not all exercises are created equal. Some exercises are more effective at stimulating bone growth and increasing bone density. Understanding which type of exercise contributes most to building strong bones can help you design a fitness routine that promotes optimal bone health.
Weight-Bearing Exercises
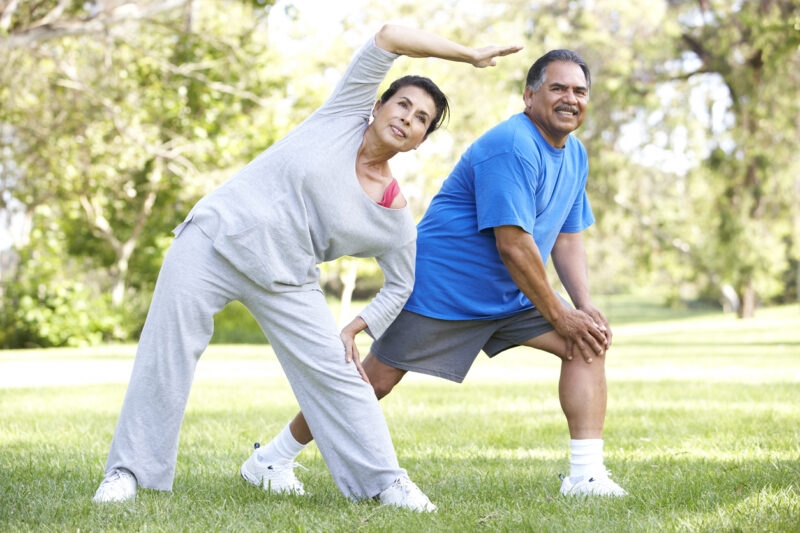
Weight-bearing exercises, which force your body to work against gravity, are among the best for building strong bones. These exercises include activities like walking, jogging, dancing, and hiking. When you engage in these movements, your bones experience a healthy amount of stress, which stimulates bone cells to grow stronger and denser. Weight-bearing exercises focus on the lower body, targeting the bones in your hips, legs, and spine—areas most vulnerable to fractures as you age.
Resistance Training
Resistance training, or strength training, is another highly effective way to build bone strength. Exercises like lifting weights, using resistance bands, or performing bodyweight exercises (e.g., squats, lunges, and push-ups) apply direct force to your muscles and bones. This encourages the bones to adapt by becoming denser. Resistance training can target both the upper and lower body, making it a versatile choice for improving overall bone health.
High-Impact vs. Low-Impact
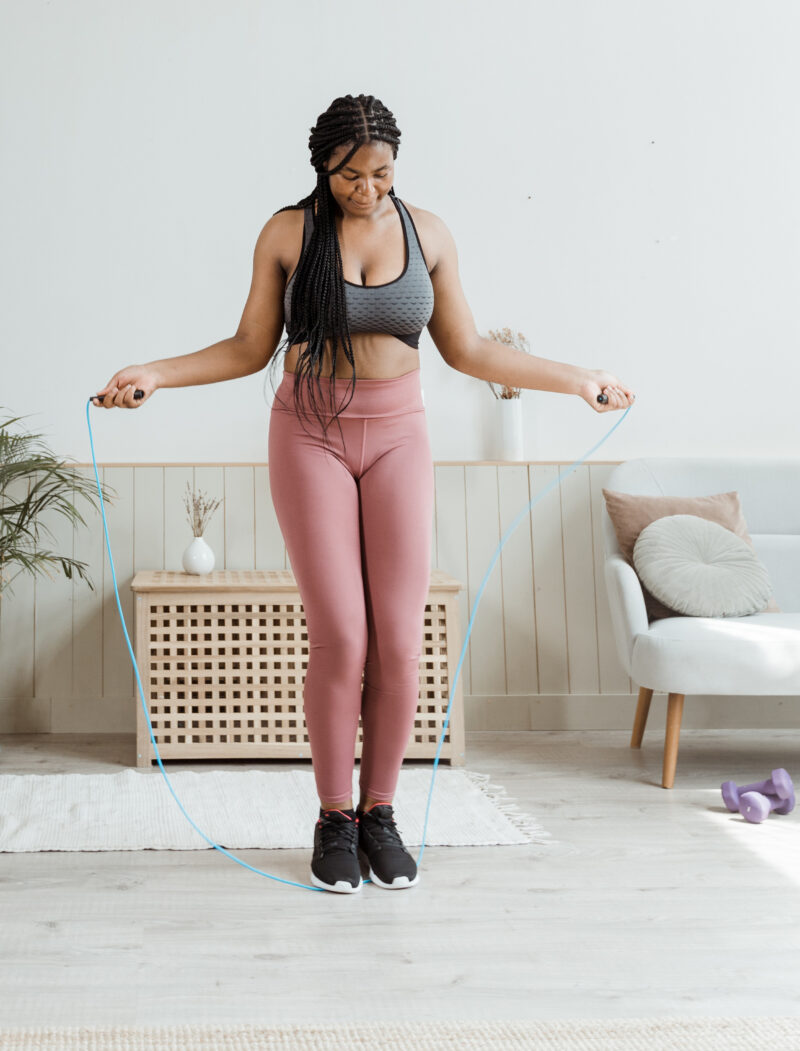
High-impact activities like running, tennis, and jumping rope offer significant benefits for bone density, especially in weight-bearing areas. However, low-impact exercises such as swimming or cycling, while excellent for cardiovascular health, do less for bone building since they don’t put enough stress on the bones.
Building a Balanced Routine
To maximize bone health, incorporate a mix of weight-bearing and resistance exercises into your routine. These activities not only strengthen your bones but also improve muscle function, balance, and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and fractures as you age. By focusing on the type of exercise that contributes most to building strong bones, you can take proactive steps to ensure your bone health for years to come.

Weight-Bearing Exercises: The Key to Building Bone Strength
Weight-bearing exercises play a crucial role in building strong bones, making them one of the most effective answers to which type of exercise contributes most to building strong bones. These exercises force your body to work against gravity, which applies stress to the bones and stimulates growth. The impact and pressure from your body weight challenge the bones, encouraging them to become stronger and denser over time.
High-Impact Weight-Bearing Exercises
High-impact weight-bearing exercises include activities like running, hiking, tennis, and jumping rope. These movements create more force on the bones, particularly in the legs, hips, and spine. For example, the repetitive impact from running or jumping sends signals to bone cells (osteoblasts) to build new bone tissue. This continuous rebuilding process increases bone density and reduces the risk of fractures.
Incorporating high-impact exercises into your routine a few times a week can significantly enhance bone strength. However, it’s essential to start gradually, especially if you’re new to high-impact activities, to avoid injury. Always ensure proper technique and consider working with a trainer if needed.
Low-Impact Weight-Bearing Exercises
Low-impact weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, brisk walking, and dancing, are excellent alternatives for those who may have joint concerns or are just starting their fitness journey. While these exercises apply less force than high-impact activities, they still provide enough stress to stimulate bone growth. Walking, for instance, targets the bones in the lower body and can be easily incorporated into your daily routine. This makes it a great long-term, sustainable way to maintain bone health.
Both high- and low-impact weight-bearing exercises serve as foundational movements in any bone-strengthening program. The key is consistency and ensuring that these exercises become a regular part of your lifestyle. By engaging in these activities, you provide your bones with the regular stress they need to remain strong and resilient, making weight-bearing exercises a central answer to which type of exercise contributes most to building strong bones.
Resistance Training for Bone Density Improvement
Resistance training, also known as strength training, is a highly effective method for increasing bone density. It stands out as a crucial answer to which type of exercise contributes most to building strong bones. By engaging muscles and bones under tension, resistance training encourages the body to strengthen its skeletal structure. This type of exercise targets both upper and lower body bones, helping to enhance overall bone health.
How Resistance Training Improves Bone Density
Resistance training involves exercises that force muscles to contract against an external force, such as weights, resistance bands, or bodyweight. This process puts direct pressure on bones, stimulating bone-forming cells (osteoblasts) to rebuild and strengthen the bone tissue. The more you challenge your muscles and bones through resistance exercises, the more bone density improves, especially in areas vulnerable to fractures, such as the hips, spine, and wrists.
For example, exercises like squats, lunges, and deadlifts directly stress the bones in the legs, hips, and spine, while push-ups and rows target the bones in the arms and shoulders. Regularly incorporating these movements into your routine ensures you work the key bone-supporting areas of the body. As muscles grow stronger, they apply even more force to the bones, further enhancing the strengthening effect.
Types of Resistance Training for Bone Health
There are several types of resistance training that contribute to building strong bones. Free weights, such as dumbbells and barbells, offer a versatile way to engage multiple muscle groups and bones. Machines can provide controlled resistance, helping beginners safely practice movements. Bodyweight exercises, like squats, push-ups, and planks, also apply significant pressure to bones and are easy to perform anywhere.
For optimal bone health, aim for resistance training at least two to three times per week. Vary your exercises to target different muscle and bone groups, ensuring you build strength and bone density throughout the body. Resistance training not only helps improve bone density but also strengthens muscles, enhances balance, and reduces the risk of falls—making it an essential component of any bone-strengthening routine. With the proper approach, resistance training remains one of the most effective answers to which type of exercise contributes most to building strong bones.
High-Impact vs. Low-Impact Exercises: Which is Best for Bone Health?
When determining which type of exercise contributes most to building strong bones, the distinction between high-impact and low-impact exercises becomes critical. Both forms of exercise benefit bone health, but they vary in intensity and effectiveness. Understanding which type is best for your needs can help you create a more effective bone-strengthening routine.
High-Impact Exercises: Maximizing Bone Growth
High-impact exercises, such as running, jumping, and tennis, involve intense, repetitive forces that directly stimulate bone growth. These activities apply greater stress to the bones, which triggers bone-forming cells (osteoblasts) to strengthen and thicken bone tissue. High-impact exercises are particularly effective for building bone density in the lower body, especially in the hips, legs, and spine.
However, high-impact activities may not be suitable for everyone, especially individuals with joint issues or those at risk for injury. While these exercises provide faster bone-strengthening results, they also place greater strain on joints, requiring proper technique and gradual progression.
Low-Impact Exercises: A Gentle but Effective Approach
Low-impact exercises, such as brisk walking, cycling, and yoga, offer a gentler approach to building strong bones. Although these activities do not apply as much force on the bones as high-impact exercises, they still provide enough stress to stimulate bone growth over time. Low-impact exercises are ideal for those with joint concerns or beginners who are gradually building up their strength.
While they may take longer to produce visible improvements in bone density, low-impact exercises have the added benefit of being more sustainable and less likely to cause injury. Walking, in particular, can be done daily, helping to maintain bone health without overloading the body.

Choosing the Best Approach
For optimal bone health, incorporating both high-impact and low-impact exercises can create a balanced routine. High-impact exercises offer rapid bone-building benefits, while low-impact exercises provide consistent, safe stimulation. The best approach depends on your fitness level, bone health goals, and personal preferences. By combining both types, you can ensure a comprehensive strategy for long-term bone strength, answering the question of which type of exercise contributes most to building strong bones in a personalized way.
How Often Should You Exercise to Build Strong Bones?
Frequency plays a crucial role when considering which type of exercise contributes most to building strong bones. The body needs consistent, yet varied, stimuli to strengthen bones and maintain bone density over time. However, overdoing it can lead to injury or excessive strain, making it essential to find the right balance.
Ideal Frequency for Weight-Bearing Exercises
For weight-bearing exercises like walking, jogging, or hiking, aim for at least 4-5 days per week. These activities provide a moderate, consistent impact on the bones, especially in the lower body. For beginners, start with 20-30 minutes of brisk walking and gradually increase the duration and intensity as your strength and endurance improve. Weight-bearing exercises are generally safe to do frequently since they are lower in intensity compared to high-impact activities, but they still help build and maintain bone density.
Resistance Training Frequency
For resistance training, focusing on strength and bone density, aim for 2-3 sessions per week. These workouts should target different muscle and bone groups, allowing for recovery between sessions. For example, focus on upper body exercises one day (e.g., push-ups, rows), and lower body exercises (e.g., squats, lunges) the next. Recovery is crucial in resistance training because bones need time to rebuild and strengthen after being stressed.
Over time, you can gradually increase the resistance or weight used to continuously challenge your bones and muscles. This ensures progressive bone strength without overwhelming the body.
Mixing High- and Low-Impact Exercises
Incorporating both high-impact and low-impact activities into your weekly routine maximizes the benefits of both. High-impact exercises, such as running or jumping, can be done 1-2 times a week for bone growth, while low-impact activities, such as walking or yoga, can be added more frequently to maintain flexibility and bone strength.
By balancing these exercise types and finding the right frequency, you provide your bones with the variety they need for optimal health. The key is consistency, not intensity, in determining which type of exercise contributes most to building strong bones.
The natural bone strength complex made from Satsuma mandarin orange
Juveriente®’s Bone Strength Complex is a natural supplement made from a traditional dietary habit of a healthy bone town in Japan. People there eat a lot of Satsuma mandarin orange and have high concentration of Beta-Cryptoxanthin, a kind of carotenoid. A cohort study there found that that concentration has high reverse correlation with onset ratio of osteoporosis.
It provides you the essence of a natural food, which is simply an extract of a Japanese popular citrus fruit. It is according to your principal policy. Needless to say, it is better to try a natural food before jumping to strong medicines. Though natural and gentle, it has garnered a lot of amazing reviews in Amazon since its launching in 2016.
This natural supplement contains most of the minerals discussed above. If you are to try multi-vitamin for your bone health, Juveriente® Bone Strength Complex will provide you most of the vital minerals as well as the Japanese bone health secret.
Please learn details in our product page.